Introduction:
Behind the myriad products and complex processes in the industrial world, catalysts silently play an essential role. By accelerating chemical reactions without being consumed, they drive efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in various industries.
1. Catalysts Defined: More Than Just Speed Boosters
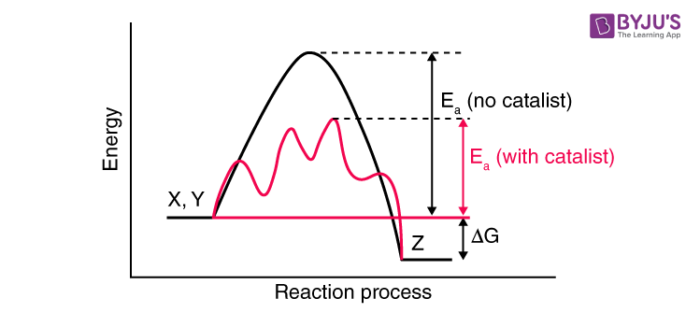
Catalysts are substances that enhance the rate of chemical reactions without undergoing permanent chemical change themselves.
- Lowering Activation Energy: Catalysts operate by reducing the energy required to initiate a reaction, enabling reactions to proceed faster or at lower temperatures.
- Economic Impact: Faster reactions often mean shorter production times and reduced energy costs, translating to economic benefits.
2. Petroleum Refining: Cracking and Reforming
One of the most notable uses of catalysts is in the petroleum industry.
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking: Here, heavy hydrocarbon fractions are broken down into lighter, valuable products like gasoline and diesel.
- Catalytic Reforming: This process enhances the octane rating of naphtha to produce high-octane gasoline.
3. Environmental Protection: Catalysts at the Forefront
Addressing environmental concerns, catalysts play a vital role in reducing harmful emissions.
- Automobile Exhaust: Catalytic converters transform toxic pollutants in car exhaust into harmless nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Industrial Emissions: Catalysts aid in treating harmful emissions from factories, ensuring cleaner air.
4. Chemical Industry: A Catalyst-Driven Realm
Numerous everyday products owe their existence to catalyst-driven processes.
- Polymer Production: Catalysts are vital in producing polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene, foundational for a multitude of plastic products.
- Fertilizers: The Haber-Bosch process, reliant on catalysts, enables the mass production of ammonia, a crucial ingredient in fertilizers.
5. Food and Beverages: Enzymatic Catalysts at Play
Natural catalysts, enzymes, have a significant role in the food and beverage industry.
- Brewing: Enzymes convert starches into fermentable sugars, essential for producing beer and spirits.
- Dairy: Lactase, an enzyme, breaks down lactose, enabling the production of lactose-free products.
6. Pharmaceuticals: Expediting Drug Synthesis
Catalysts are indispensable in drug development and production.
- Efficient Synthesis: Catalysts allow for faster and more efficient production of pharmaceutical compounds, ensuring timely delivery to those in need.
- Innovation: New catalytic methods can lead to novel drug synthesis routes, potentially unlocking new therapies.
7. Sustainable Production: Catalysts Leading the Green Revolution
In our quest for sustainability, catalysts are champions of green industrial processes.
- Reduced Waste: Catalytic processes often have fewer by-products, leading to minimized waste.
- Energy Efficiency: By operating at lower temperatures and pressures, catalysts can significantly reduce energy consumption.
8. Future of Catalysts: Nanotechnology and Beyond
The future of catalysis is rife with promise, with new technologies pushing boundaries.
- Nanocatalysts: Nanotechnology is ushering in catalysts with increased surface areas and enhanced efficiency.
- Biocatalysis: Using nature’s own catalysts, enzymes, industries can achieve more environmentally friendly processes.
Conclusion:
The role of catalysts in industrial processes is profound, often working behind the scenes to ensure efficiency, sustainability, and innovation. As industries evolve and new challenges emerge, the importance of these remarkable substances will only grow, cementing their status as unsung heroes of the industrial realm.
Tags: #Catalysts, #IndustrialProcesses, #ChemicalReactions, #PetroleumRefining, #EnvironmentalProtection, #PolymerProduction, #SustainableProduction, #Nanocatalysts