Chemical kinetics is the study of how and at what rate chemical reactions occur. It delves into the factors that influence the speed of reactions, shedding light on the dynamic nature of chemical processes. This article embarks on a journey through the realm of chemical kinetics, exploring concepts like reaction rates, activation energy, and the pivotal role of catalysts. From the collision theory to the intricacies of reaction mechanisms, we unravel the fascinating intricacies that govern the pace of chemical transformations.
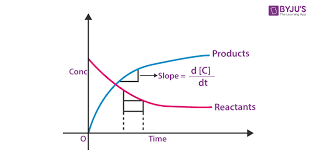
1. Unraveling Reaction Rates: A Measure of Change
Reaction rate is a crucial parameter that quantifies the speed at which reactants are converted into products, providing insights into the kinetics of a reaction.
2. Collision Theory: The Dance of Molecules
The collision theory postulates that effective collisions between reactant molecules are a prerequisite for a chemical reaction to occur.
3. Activation Energy: Overcoming the Barrier
Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction by breaking bonds in the reactant molecules.
4. Rate Laws: Quantifying Reaction Rates
Rate laws provide mathematical expressions that relate the reaction rate to the concentrations of reactants, offering predictive power.
5. Rate-Determining Step: The Slowest Link
In complex reactions, the rate-determining step is the slowest step that determines the overall rate of the reaction.
6. Reaction Mechanism: The Pathways of Change
The reaction mechanism describes the series of elementary steps by which reactants are transformed into products.
7. Catalysis: Accelerating Reactions
Catalysts are substances that facilitate chemical reactions by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy.
8. Homogeneous vs. Heterogeneous Catalysis: Catalysts at Work
Catalysts can be classified as homogeneous (in the same phase as reactants) or heterogeneous (in a different phase), each with distinct mechanisms.
9. Enzyme Catalysis: Nature’s Catalysts
Enzymes are biological catalysts that play a fundamental role in facilitating biochemical reactions in living organisms.
10. Factors Influencing Reaction Rates: Beyond Catalysts
Temperature, concentration, pressure, and surface area are among the factors that impact reaction rates, offering control over chemical processes.
11. Reaction Kinetics in Industry and Nature
Understanding chemical kinetics is paramount in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to food processing, where reaction rates dictate product yields and quality.
In Conclusion: Decoding Chemical Dynamics
Chemical kinetics unravels the intricate dance of molecules, providing a profound understanding of reaction rates and mechanisms. It empowers scientists and engineers to control and optimize chemical processes, from the laboratory bench to industrial scales. By comprehending the speed of reactions, we unlock the potential to drive innovation and shape the world around us.
In Conclusion:
Chemical kinetics unravels the intricate dance of molecules, providing a profound understanding of reaction rates and mechanisms. It empowers scientists and engineers to control and optimize chemical processes, from the laboratory bench to industrial scales. By comprehending the speed of reactions, we unlock the potential to drive innovation and shape the world around us.