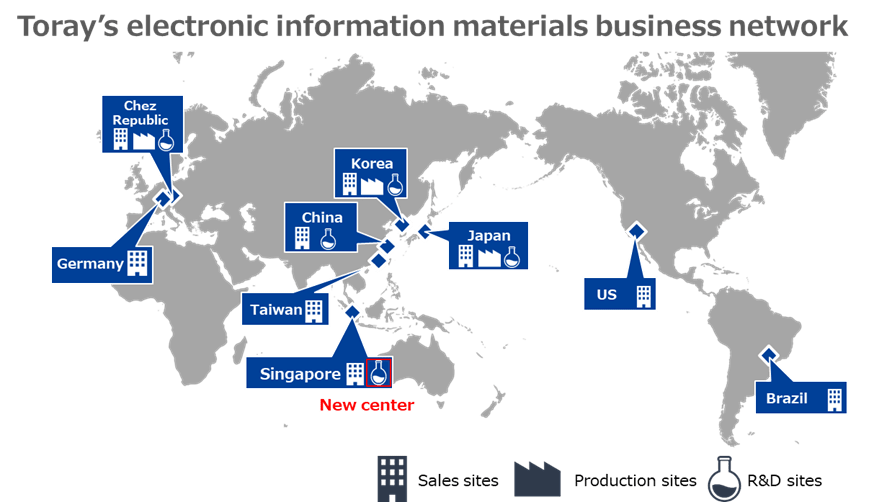
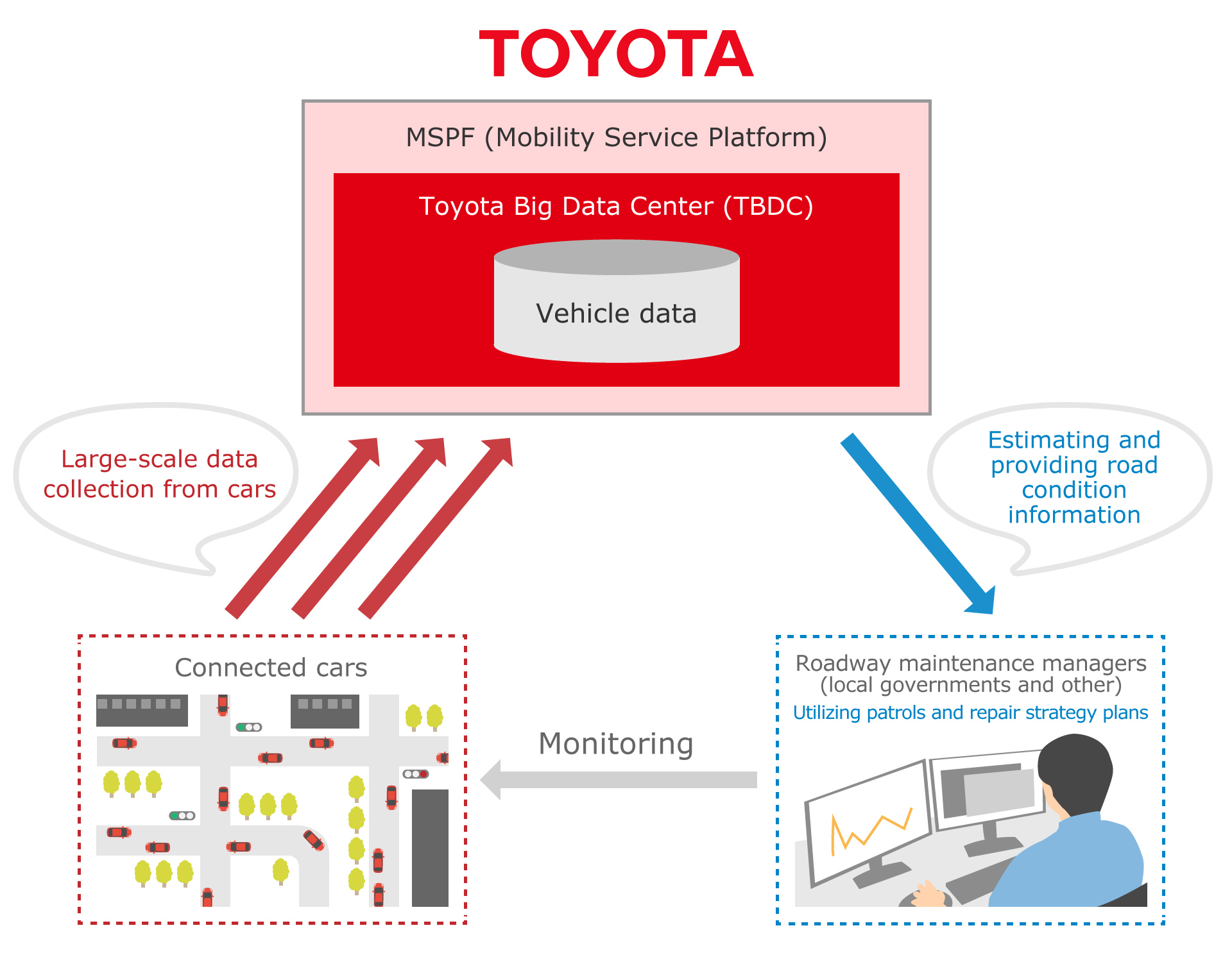
Colors have a profound impact on our world, influencing emotions, aesthetics, and even functionality. Yet, the vibrant palette we encounter daily is the result of intricate chemical processes. This comprehensive guide will illuminate the chemistry behind colors, from the pigments found in nature to the synthetic dyes that have revolutionized industries.
**1. Color Perception and Vision: A Complex Interplay
a. The Human Eye and Color Sensation: Understanding how our eyes perceive and interpret different wavelengths of light.
b. Color Theory: Exploring the principles of color mixing and the relationships between primary, secondary, and tertiary colors.
**2. Natural Pigments: Nature’s Palette
a. Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis: The green pigment that drives the process of photosynthesis in plants.
b. Carotenoids and Anthocyanins: Pigments responsible for the vibrant hues of fruits and vegetables.
**3. Mineral Pigments: Earth’s Hidden Colors
a. Iron Oxides and Ochres: The natural pigments that give earthy tones to rocks, soils, and ancient artworks.
b. Ultramarine Blue and Lapis Lazuli: Precious blue pigments derived from minerals like lapis lazuli.
**4. Animal-Derived Colors: Nature’s Intricate Hues
a. Tyrian Purple: An ancient and rare purple dye extracted from sea snails.
b. Cochineal Red: Derived from crushed insects, this vivid red dye has been used for centuries.
**5. Synthetic Dyes: Revolutionizing Color Production
a. William Henry Perkin and Mauveine: The accidental discovery of the first synthetic dye, revolutionizing the textile industry.
b. Aniline Dyes and the Birth of the Chemical Industry: How the development of synthetic dyes spurred the growth of the chemical industry.
**6. Chemical Structure of Colorants
a. Conjugated Systems and Color: Exploring the molecular structures that give rise to vibrant colors.
b. Absorption and Reflection of Light: Understanding how molecules absorb and reflect specific wavelengths of light to produce color.
**7. Applications of Color in Art and Industry
a. Pigments in Painting: The use of natural and synthetic pigments in creating enduring works of art.
b. Coloration of Textiles and Fashion: How dyes and pigments enhance fabrics with an array of vivid shades.
**8. Dyeing Techniques: Mastering Color Application
a. Dip Dyeing and Immersion Dyeing: Techniques for achieving uniform coloration of fabrics.
b. Tie-Dye and Batik: Artistic methods that create unique and intricate patterns through selective dye application.
**9. Colorfastness and Lightfastness: Ensuring Longevity
Understanding how dyes and pigments withstand fading or bleeding when exposed to various environmental conditions.
**10. Innovations in Color Chemistry
a. Nanotechnology in Colorants: Manipulating materials at the nanoscale for new and unique color effects.
b. Sustainable Dyeing Methods: Exploring eco-friendly alternatives to traditional dyeing processes.
**11. Color in the Digital Age: Display Technologies
How chemical innovations have led to the creation of vivid displays in devices like TVs, smartphones, and monitors.
Conclusion: Colors as a Chemical Symphony
The world of colors is a testament to the artistry of chemistry. By delving into the molecular intricacies of pigments and dyes, we gain a deeper appreciation for the vibrant tapestry that surrounds us. From the natural wonders of the earth to the synthetic marvels of the laboratory, colors continue to captivate our senses and inspire creativity across disciplines and danatoto industries.