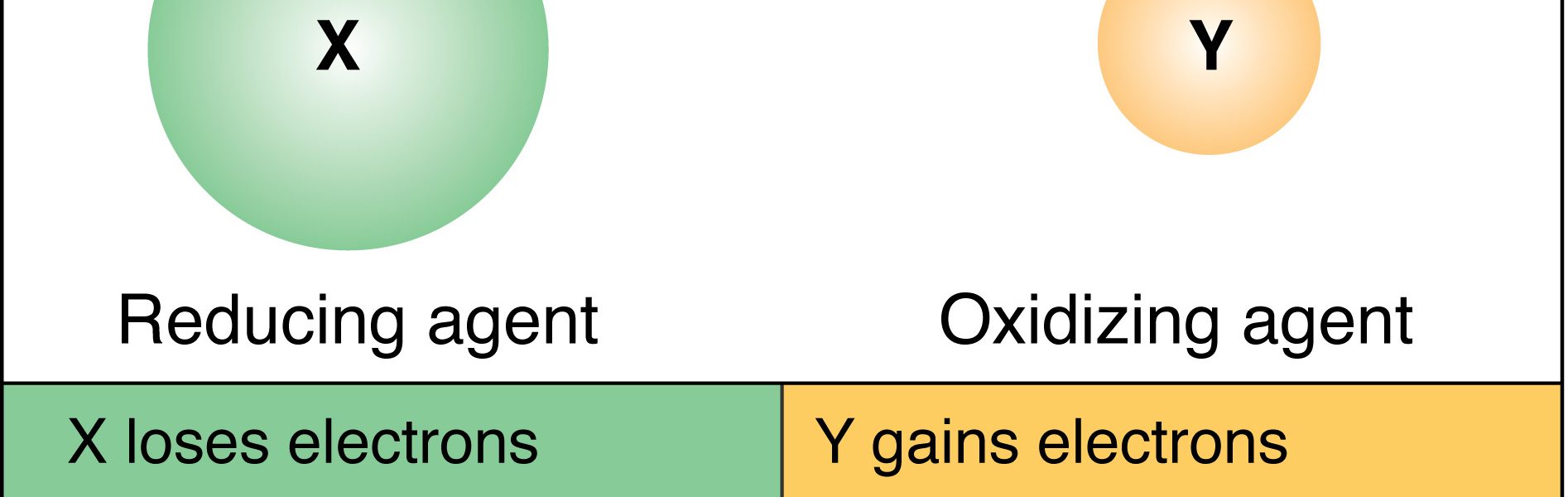
Oxidation and reduction, collectively known as redox reactions, are fundamental processes that underpin a wide array of natural phenomena. These chemical reactions involve the transfer of electrons between substances, leading to transformations that range from the sweet ripening of fruit to the relentless advance of rust. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the profound impact of oxidation and reduction in various natural processes, shedding light on their diverse roles in shaping our world.
1. Unraveling the Basics: Oxidation and Reduction Defined
a. Electron Transfer: Understanding how electrons change hands between atoms and molecules, driving redox reactions.
b. Oxidation Numbers: Defining the formalism used to track electron movement in chemical compounds.
2. Redox Reactions in Biological Systems
a. Cellular Respiration: How organisms extract energy from food through a series of redox reactions.
b. Photosynthesis: The intricate dance of electron transfer that powers the synthesis of glucose and oxygen in plants.
3. Fruit Ripening: A Tasty Example of Redox Reactions
a. Ethylene Gas and Ethene Oxide: How the ripening hormone ethylene orchestrates the transformation of green, unripe fruit into vibrant, flavorful edibles.
b. Color Changes and Flavor Development: The chemical reactions that bring about the visual and taste transformations during fruit ripening.
4. Rusting Away: Oxidation in Corrosion
a. Iron Oxidation: The process by which iron reacts with oxygen and water to form rust, a common example of corrosion.
b. Prevention and Mitigation: Strategies employed to protect metal structures from the damaging effects of rust.
5. Oxidation-Reduction Potential: A Measure of Reactivity
a. Quantifying Redox Reactions: How scientists and engineers use oxidation-reduction potential to predict the behavior of chemical reactions.
b. Applications in Industry and Environmental Engineering: Redox potential’s role in processes ranging from wastewater treatment to metallurgy.
6. Beyond Chemical Reactions: Oxidation-Reduction in Industry
a. Bleaching Processes: How redox reactions are harnessed to remove color from substances like paper pulp and textiles.
b. Water Treatment: The use of redox reactions to eliminate contaminants from water, ensuring safe drinking sources.
7. Environmental Implications of Redox Reactions
a. Bioremediation: The use of microbial redox reactions to clean up environmental pollutants, from oil spills to groundwater contamination.
b. Nitrogen Cycle: How redox reactions play a crucial role in the cycling of nitrogen compounds in soil and water ecosystems.
8. Harnessing Redox Reactions for Innovation
a. Fuel Cells and Batteries: The technology that leverages electron transfer in chemical reactions to generate electricity.
b. Green Chemistry: How the principles of oxidation and reduction contribute to the development of sustainable, eco-friendly chemical processes.
Conclusion: The Dance of Electrons in Nature
Oxidation and reduction are the choreographers of countless natural transformations, orchestrating processes from the mundane to the monumental. Understanding the profound impact of redox reactions offers insights not only into the intricate chemistry of our world but also into the potential for harnessing these processes for innovative solutions. From fruit ripening to rust, the dance of electrons shapes the world we know, providing a powerful lens through which we can comprehend and manipulate the processes that define our danatoto environment.