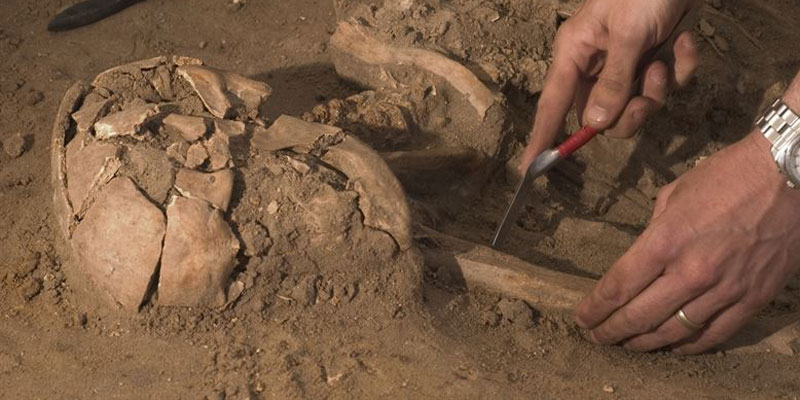
As the old adage goes, “history is written by the victors.” But often, what’s left behind are the physical remnants of cultures long gone. From pottery fragments to bones, from metallic objects to ancient textiles, these artifacts provide invaluable insights into our past. But how do we extract these stories? Enter the symbiotic relationship between archaeology and chemistry. Together, they reconstruct, preserve, and decode historical danatoto narratives with unparalleled precision.
1. Introduction:
While archaeology excavates and interprets material culture from bygone eras, chemistry helps decode the mysteries these relics hide. The techniques derived from chemistry can determine the age, origin, usage, and even the decay of archaeological finds.
2. Radiocarbon Dating:
Perhaps the most renowned application of chemistry in archaeology, radiocarbon dating measures the decay of carbon isotopes in organic materials. By understanding the half-life of carbon-14 and its ratio to carbon-12 in an artifact, archaeologists can estimate the age of an object, sometimes up to 50,000 years old.
3. Elemental Analysis:
- X-ray Fluorescence (XRF): By directing X-rays onto an artifact, the subsequent emitted fluorescence helps identify elements present. This can reveal the provenance of metals or the origin of pigments in pottery.
- Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA): This technique determines the composition of clay or metals, helping trace an artifact’s origin.
4. Spectroscopy in Artifact Analysis:
Techniques like infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy help in identifying the molecular composition of samples. Whether it’s revealing the components of ancient paints, inks, or organic materials, spectroscopy offers a non-destructive way to analyze artifacts.
5. Bioarchaeology and DNA Analysis:
Chemistry plays a pivotal role in bioarchaeology. DNA extraction from ancient remains, studying isotopic ratios in bones to discern diet, or analyzing ancient proteins are all rooted in chemical techniques. Such analysis provides insights into ancient health, migration patterns, and even relationships between individuals.
6. Preservation of Artifacts:
From preventing metal corrosion to ensuring organic materials like textiles or parchment don’t disintegrate, chemistry offers solutions to preserve artifacts. Chemical analysis can inform the best environmental conditions for artifact storage or identify the right solvents to clean and maintain them.
7. Reconstructing Ancient Technologies:
Chemistry aids in understanding the techniques ancient civilizations employed. For instance:
- Metalworking: Elemental and isotopic analysis can reveal ancient smelting, alloying, and casting methods.
- Textile Dyeing: By identifying dye molecules on ancient textiles, chemists can infer the dyeing techniques and materials used.
8. Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
While chemical methods provide invaluable insights, they come with challenges. Some techniques might be invasive or destructive. Additionally, given the sacred significance of certain artifacts, especially human remains, ethical considerations about their handling and analysis become paramount.
9. Conclusion:
Chemistry, in tandem with archaeology, forms a bridge connecting the present to the past. Each artifact, with its unique chemical signature, tells tales of ancient societies, their practices, innovations, and histories. As technology advances, the collaboration between these two disciplines will only deepen, bringing the past into clearer focus. By peeling back the layers of time chemically, we’re not just understanding our ancestors better but also appreciating the intricate tapestry of human history.
Tags:
#ChemistryInArchaeology #RadiocarbonDating #ArtifactPreservation #ElementalAnalysis #AncientHistories
Chemistry and archaeology, though seemingly disparate fields, come together to weave narratives of our ancient past. From determining the age of relics to reconstructing ancient technologies, the intricate dance between these disciplines provides a comprehensive understanding of human history. Whether you’re an archaeology enthusiast, a chemistry buff, or someone curious about our shared heritage, this confluence of science and history promises rich insights into the annals of time.