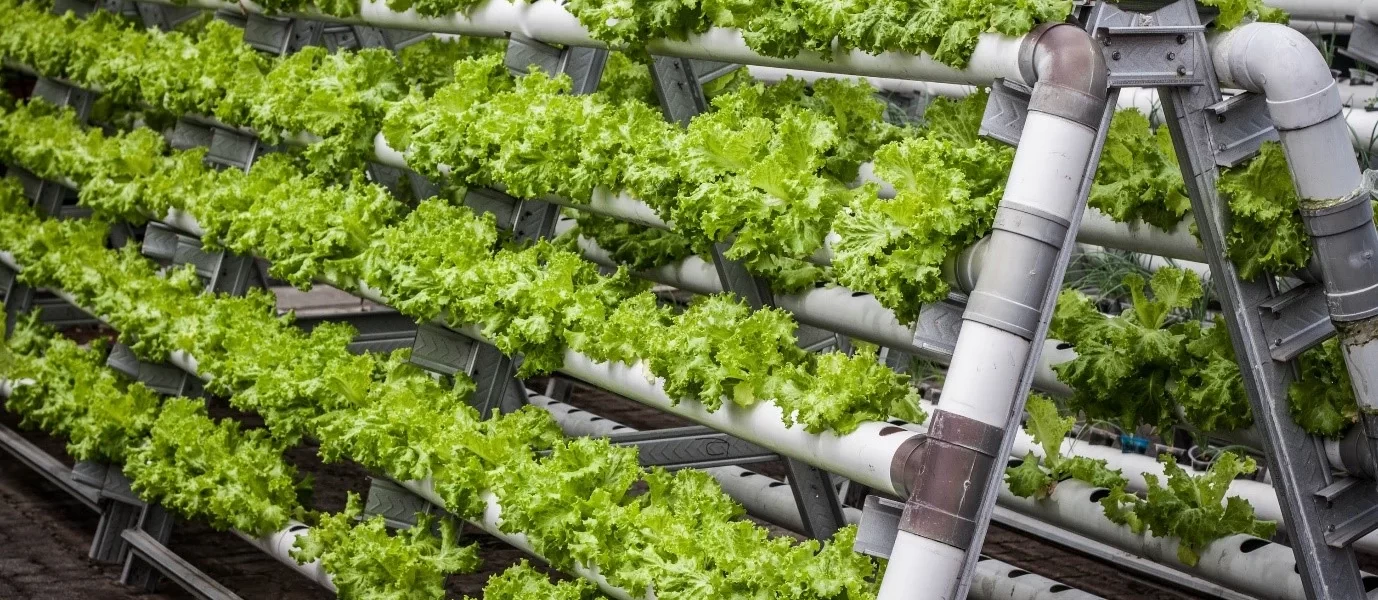
Today, as the world is subject to increased urbanization, the intricacy of feeding a larger population has also escalated. However, a nuanced and innovative solution is taking root: Vertical farming. Via smart and sustainable systems and technologies, vertical farming promotes an efficient way of growing food in the city. The farms utilize vertical space to produce vast quantities of fresh produce without a huge amount of land that is used.
Vertical farming refers to the practice of farming in vertically stacked layers, often integrated into controlled environments like those found in buildings using warehouses or shipping containers. The technology helps farm owners to regulate the environmental aspects such as temperature, light, humidity, and nutrient levels, among others. As a result, crops grow faster, have a higher yield, and plants can be harvested throughout the year. As a result, vertical farming can, through indoor production, address the food security issue, reduce the importation of perishable commodities, and promote accessible fresh locally grown food. The adoption of vertical farming offers a better approach to ensuring fooding for the future is sustainable.
Advantages of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming can be an effective solution to urban food challenges while also providing the following benefits: higher yields. Stacking crops in a vertical farm enables the farming of significantly more produce than traditional farming on the same land. Given that land is a limiting, but growing source, vertical farming could be an effective measure to meet the increasing food demand in urban areas. Year-round growth. Vertical farming relies on controlled-environment agriculture that provides necessary and optimal growing conditions to any produce grown in a farm.
As most of the conditions are controlled, it is possible to farm food regardless of the outside climate, which ensures that fresh produce is available year-round. This would eliminate the need to transport foods over long distances, which would reduce food miles and the corresponding carbon footprint. Water conservation. Vertical farms also require much less water usage than traditional farms. Most of them use hydroponic or aeroponic systems that do not use soil and enable the recirculation of water. As a result, it reduces loss and contamination, thereby conserving water from soil erosion and contamination.
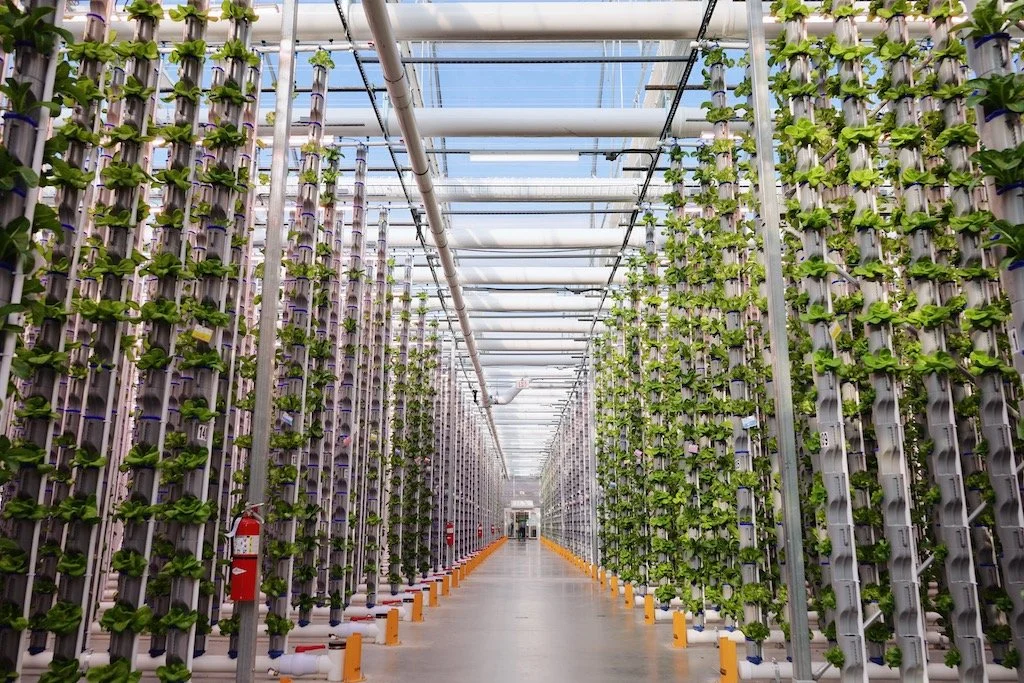

Challenges in Urban Food Production
Despite the vast potential, urban food production is characterized by several challenges that limit its capability to satisfy the growing population’s needs. The first limitation is the availability of land in emergent urban centers. Whereas most urban cities start as rural areas, the increasing urbanization has transformed multiple food production zones into towns, losing much of the space utilized for farming. The soil quality has also deteriorated significantly due to pollution and environmental degradation, which reduce the efficiency of conventional methods.
The second limiting factor in the opportunities of importation. Most urban centers do not produce enough food to feed their populations. Thus, food must be brought from distant hinterlands, increasing the green gas emissions and the risks of failure of the global food systems. Lastly, the conventional methods used in rural zones have proved inefficient due to high utilization of water and chemicals being detrimental to the ecosystem. Thus, there is a need to develop novel farming technologies to optimize urban food production.
How Vertical Farming Addresses Urban Food Challenges
Vertical farming has multiple implications that serve to address the problem of urban food production.
Firstly, it helps to optimize land use, which is vital for highly populated urban places. As vertical crops grow upwards, farmers can achieve higher yields per meter than in the case of traditional horizontal farming. It implies that vertical farming can make the best use of limited urban areas and supply the city with a substantial amount of fresh food.
Second, vertical farming helps reduce the dependency on imported fruits and vegetables. By growing food locally, cities create a chance to receive more fresh food on their own without the need to order it from distant places. It promotes food security and reduces the negative implications of carbon dioxide transport emissions.
Finally, vertical farming can help minimize the environmental footprint of food production. Controlled growing conditions allow farmers to best utilize resources and minimize waste levels. For example, there would be no need in using much water as indoor irrigation systems could provide pre-cultivated crops with the necessary. Fertilizers should also be optimized in the form of nutrient recycling that would promote resource efficiency.
Types of Vertical Farming Systems
Vertical farming encompasses various systems and techniques, each with its unique characteristics and advantages. One common type is the multilayer vertical farm, where crops are grown in stacked layers using hydroponic or aeroponic systems. These farms often utilize artificial lighting to provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth.
Another type is the vertical farm built within converted buildings such as warehouses or shipping containers. These farms take advantage of existing structures and can be easily scalable. They often incorporate advanced technologies like automated climate control and vertical conveyor systems for efficient crop management.
Additionally, there are rooftop vertical farms that utilize unused rooftop spaces in urban areas. These farms not only provide fresh produce but also contribute to urban greening and enhance the aesthetic appeal of buildings.
Vertical Farming Techniques and Technologies
Vertical farming relies on various techniques and technologies to optimize crop growth and maximize efficiency. One technique commonly used is hydroponics, where plants are grown in nutrient-rich water without soil. This method allows for precise control over nutrient levels, pH, and water availability, resulting in faster growth and higher yields.
Aeroponics is another technique used in vertical farming, where plants are grown in an air or mist environment without soil or water. This method provides plants with a highly oxygenated and nutrient-rich environment, leading to faster growth rates and increased nutrient absorption.
Advanced lighting systems are crucial in vertical farming, as they provide the necessary light spectrum for photosynthesis. LED lights are commonly used due to their energy efficiency and ability to provide specific light wavelengths that promote plant growth.
Vertical farming also incorporates automation and data-driven technologies. Sensors and monitoring systems allow farmers to track and control environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels. This real-time data enables farmers to make informed decisions and optimize crop growth.
Success Stories of Vertical Farming Around the World
Vertical farming has gained significant traction worldwide, with numerous success stories showcasing its potential. One notable example is AeroFarms, a vertical farm located in Newark, New Jersey. With its patented aeroponic technology and LED lighting system, AeroFarms has achieved impressive yields while using 95% less water compared to traditional farming methods. This innovative farm has demonstrated the commercial viability of vertical farming and its potential to revolutionize urban agriculture.
Another success story is Plenty, a vertical farming startup based in San Francisco. Plenty utilizes vertical hydroponics to grow a wide variety of crops, including leafy greens and herbs. By jpslot growing conditions and utilizing data-driven technologies, Plenty has been able to achieve high yields while minimizing resource usage. Their farms are strategically located near urban centers, reducing transportation costs and ensuring fresh produce reaches consumers quickly.
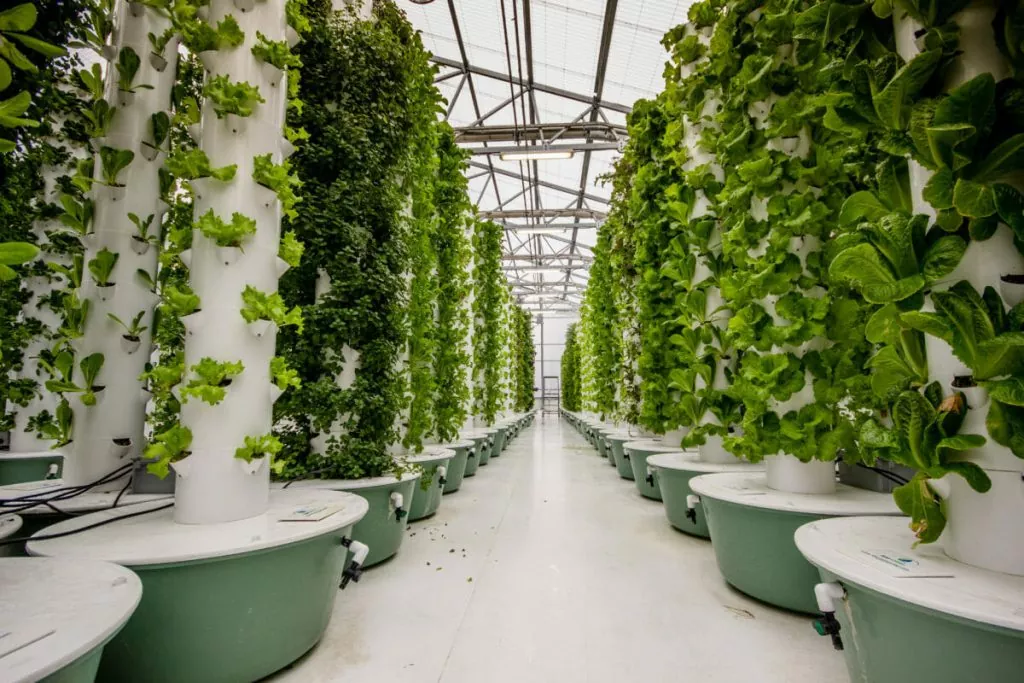

Environmental Sustainability in Vertical Farming
Environmental sustainability is a core principle of vertical farming. By utilizing controlled environments and advanced technologies, vertical farms can minimize the use of natural resources and reduce the environmental impact of food production.
One key aspect of sustainability in vertical farming is water conservation. Hydroponic and aeroponic systems recycle water, reducing overall water usage. Additionally, the absence of soil eliminates the risk of soil erosion and contamination, further protecting the environment.
Furthermore, vertical farming reduces the need for synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Integrated pest management techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects and implementing physical barriers, help control pests naturally. Nutrient recycling and precise nutrient delivery systems ensure that plants receive the necessary nutrients without excessive fertilizer use.
Finally, vertical farming’s proximity to urban centers reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation. By growing food locally, vertical farms eliminate the need for long-distance shipping, resulting in fresher produce and reduced emissions.
Economic Viability of Vertical Farming
Beyond its environmental benefits, vertical farming also holds economic potential. By utilizing vertical space and advanced technologies, vertical farms can achieve high yields and provide a consistent supply of fresh produce. This creates opportunities for commercial success and job creation within the vertical farming industry.
Vertical farming can also reduce reliance on imported produce, which can be costly due to transportation and storage expenses. By growing food locally, vertical farms can provide a more affordable and accessible food source for urban populations. This can contribute to the overall economic resilience of cities and improve food security.
Moreover, vertical farming has the potential to transform underutilized urban spaces into productive agricultural areas. By converting vacant buildings or rooftops into vertical farms, cities can revitalize unused spaces and generate additional revenue streams.
The Future of Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers a sustainable and innovative solution to address the challenges of urban food production. With its ability to maximize land utilization, reduce water usage, and provide year-round cultivation, vertical farming has the potential to revolutionize the way we grow and consume food.
As urban populations continue to grow, the demand for fresh, locally grown produce will only increase. Vertical farming can play a crucial role in meeting this demand while minimizing environmental impact. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and efficient resource utilization, vertical farming can lead us towards a healthier and more self-sufficient future. The rise of vertical farming is not just a trend but a transformative force that will shape the future of urban agriculture.
Also read: David Guetta: Membangun Legacy dalam Dunia Music Elektronik