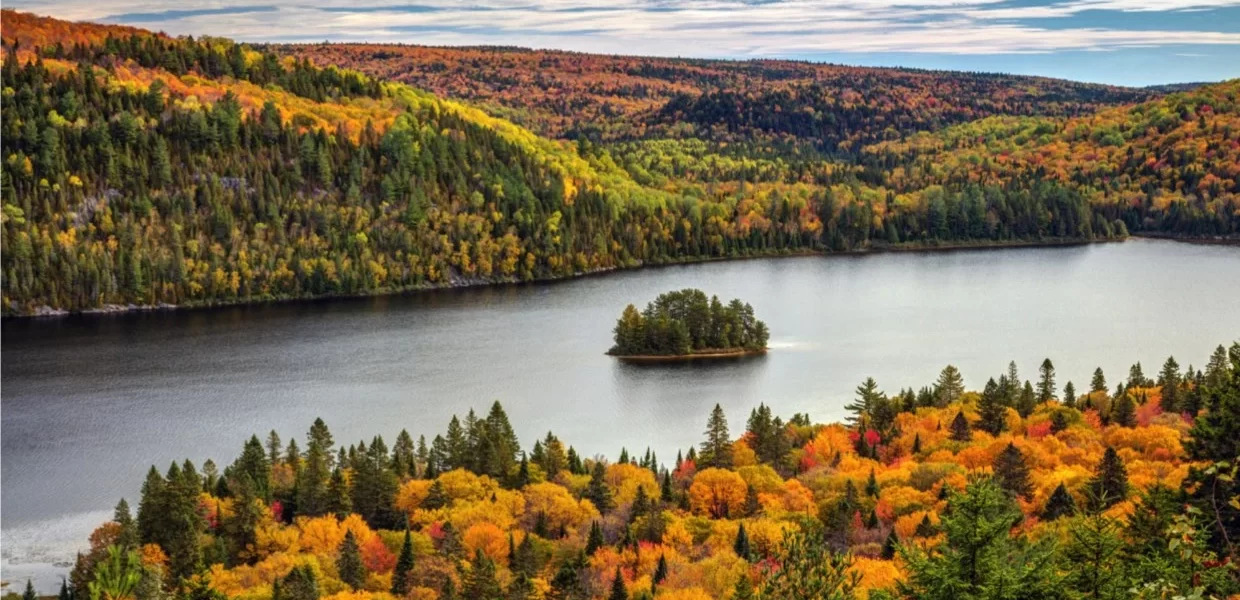
Welcome to the enchanting realm of North America’s Boreal Forests! This massive area of hinterland is shown throughout the northern parts of continent, with mystery and wonder hidden in all corners. For this article, we are exploring a even more quirky and fascinating realm.
The Boreal Forest is truly a wonder, filled with beautiful coniferous trees and sparkling lakes that are brimming over the top of wildlife. From the eerie call of a loon to the silent presence of our elusive lynx, these species are amazing residents who have all evolved to thrive in tough and cold environments.
The deeper within the heart of the Boreal Forest we investigate, however, reveals an essential nature in earth climate regulation as well as local indigenous community and global conservation needs. Learn about the need to strike a balance between human development and conservation of this fragile ecosystem, as well as how you can play your part in protecting it Lace up those hiking boots, grab some binoculars and prepare yourself for a journey through the magical land of the Boreal Forest. Let’s dive in!
Boreal Forest Ecology and Climate
The Boreal Forest, otherwise called the taiga and commonly stretching over the northern areas of North America, Europe, and Asia represents a vast wonderful terrestrial biome. The huge and varried ecosystem of Canada has a cold, continental climate with long harsh winters and short cool summers.
The average annual temperature in the Boreal Forest is -5 to 5 ºC (23-41ºF) with periodic deep freezes lasting weeks on end during winter. Rainfall and snow are the most common forms of precipitation during winter, but they tend to be low-to-moderate in level.
Nevertheless, there are a mix of plant and animal species that can tolerate these harsh conditions because they have evolved to do so in the Boreal Forest. Spruce, fir and pine trees are the dominant vegetation type of this area because these types have adapted to withstand very cold temperatures as well as enemy(Canadian Geographic Education: Boreal Forest) The lush, green foliage help provide shelter and food for a greater collection of wildlife species by supporting one-of-a-kind plant diversity.

Plants and Animals of the Boreal Forest
The Boreal Forest – features a wide variety of plant and animal species (Fig. 1) This biome predominantly consists of coniferous trees that are made up of different species such as spruce, fir, pine and larch. Adapted to the cold, dry conditions of the Boreal Forest are these tough evergreen trees that make up most of this ecosystem.
In addition to the towering conifers, decicuous trees like birch and poplar can also be found in Boreal Forest. During short but excellent summer days, the leaves on these trees grow in those beautiful green yellow gold kinds of shades that one can see all over our local land.
The region supports an extraordinarily rich diversity of wildlife, as well- some with faces that are a mirror image of other iconic species such as moose and caribou; or the grey wolf and Canada lynx. These critters have had to learn how to make it in the cold of a winter season that stretches from October into April, followed by two short months during which they must eat enough and raise young for the next long winter.
Significance of The Boreal Forest to Wildlife
In addition to the fact that it is beautiful and home to a diversity of ecosystems, the Boreal Forest contains global biodiversity significance as well provides substantial climate regulation capabilities. The Boreal Forest is the planet’s largest terrestrial biome and home to numerous plants and animals specific only to there.
The most important wildlife function of the Boreal Forest in terms of global biodiversity is providing critical nesting habitat for migrating birds. More than three billion North American birds representing hundreds of species – including warblers, sparrows, eagles and Great Blue Herons- 5 migrate to the Boreal Forest each year returning from Southern destinations to breed and raise young in areas that are virtually without predators due too isolation.
Aside from its contribution to avian biodiversity, the Boreal Forest also provides vital habitat for a large variety of other wildlife including flagship species such as moose, caribou and gray wolf. Not only do these animals appear to provide an initial benefit through increased browsing, they are also carry out keystone roles in the ecosystem – influencing landscape features and balance among food webs within Boreal Forests.
Effect of Humans on the Boreal Forest
Though the Boreal Forest has always been a major resource for indigenous people supporting their life ways in this ecosystem, there have become many modern threats and challenges to saving it as an open region. High demands for natural resources like timber, oil and minerals have resulted in extensive deforestation, habitat fragmentation and environmental desstructioin across large areas of the Boreal Forest.
Beyond the immediate impacts of resource extraction, climate change is poised to have a meaningful ecological effect on this ecosystem by influencing temperature and precipitation patterns that challenge its delicate balance. If the warming continues, however, that resilience could be compromised by a higher frequency of fires and other disturbances which can harm plant and animal communities.
Although the threats to this area are many and severe, there is hope on the horizon for Canada’s Boreal Forest. Through greater awareness and public backing for conservation measures – as well the creation of plans that promote its safekeeping, those efforts have led to a situation where this important ecosystem is being protected from extensive threats which may harm species living within. But it is working together that we can ensure the Boreal Forest remains a global stronghold, thriving and forging its invaluable biodiversity attributes and climate regulatory contributions on our planet.
Protecting the Boreal Forest
The growing realization of the importance and vulnerability of boreal forests has emerged in recent decades. It is why it has been the target of many conservation efforts by both governments and environmental organizations as well, making an effort to protect large sections because they are threatened or endangered – even though people do still make a living there.
A key conservation tactic has been the designation of protected areas like national parks and wildlife refuges throughout the Boreal Forest. The protected areas function as refuges for a range of species across the plant and animal kingdoms that depend on the robust boreal forest, protecting them from human activities such as resource extraction or infrastructure development.
In addition to establishing protected areas, there has been a strong effort at sustainable resource management within the Boreal Forest. This includes how they will do the logging and mining in a responsible way, then also some eco-tourism or low impact economic activities to sustain their financial needs while having minimal damage.
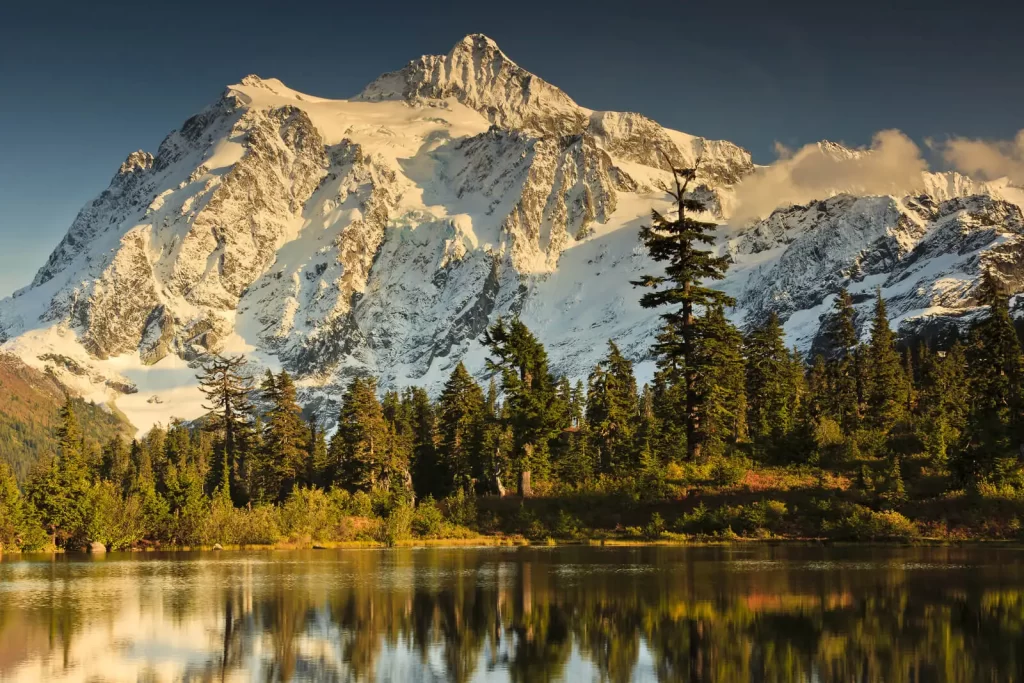

Discover the Wildlife of Boreal Forest
The myriad interesting wildlife species that call the Boreal Forest home are part of what makes it so special. From the grand moose to the elusive lynx, a majority of animals in this ecosystem have grown and evolved into types that fit well with their surroundings from those harsh conditions can be found throughout these northland regions.
Two of the Boreal’s most iconic residents are its largest mammals – moose and caribou. With long legs that easily trudge through deep snow and a thick coat to keep them warm in chilly winters, these impressive creatures have all the tools they need; perfectly adapted for life hunting amongst the labyrinthine bends of their boreal forest home.
Though the forests are predominantly associated with large mammals, they also support a range of smaller predators as well such gray wolves (Canis lupus), Canada lynx (Lynx canadensis) and wolverine. These animals are integral in the ecosystem, helping to regulate food web dynamics and manage their prey populations.
Boreal Activity Outdoor Activities
The boreal forest retail outlets a wealth of opportunities for out-of-doors enthusiasts and capabilities people alike. In the fatcai login, there are countless adventures to be had hoping and camping trip patching viewing wild life or taking photographs.
Hiking is one of the most favorite outdoor activities in Boreal Forest and you will find expansive networks that lead through thick forests, across hills and by various lakes or rivers. From rugged backcountry to tranquil old-growth forests, whether you want a heart-pounding adventure or an easy nature walk this region has something for each and every hiker.
Even in areas such as the Boreal Forest which has many campsites and great wilderness, some guided tours offer bush walking hike experiences. Sleeping in a boutique tent below towering conifers and stargazing under the impressive night time blanket of stars makes camping in Canada’s boreal woodland an unforgettable experience and unique way to immerse yourself with nature.
Ways of Life: Boreal Cultures
The Boreal Forest always been fundamental to the survival and cultures of Indigenous people over thousands years. From the Inuit of the Arctic to The Ojibwe and Cree Nations who have peacefully co-existed with mother earth in central boreal forests for centuries, all these peoples share an intimate relationship with their environment.
For a lot of indigenous people, the Boreal Forest is more than just somewhere to live. The traditional hunting, fishing and gathering practices have been sustaining these communities for centuries that they assume a deep love of nature which both respects the natural environs in their midst.
The importance of aboriginal knowledge and stewardship in the conservation/management for some areas within the Boreal Forest has been recognized to an increasing extent over recent years. Indigenous communities are playing an increasingly critical role in these efforts, as more and more traditional stewards promote mechanisms to protect the land from further damage while upholding traditions that have allowed their health for generations.
The Boreal Forest is an enchanting ecosystem that covers a huge expanse of land in the northern lands across North America, and has its own role as one can say on the Global stage. The Boreal Forest, with its towering coniferous trees and myriad of fascinating wildlife is a living symbol to the power and glory that can be found on this earth.
While we celebrate the marvels of the Boreal, it is important to recognize that this complex system remains at risk and under some serious pressures. From the impacts of human activity to climate change and the balance between conservation versus sustainable development – saving one of North America’s most critical ecosystems will require a collective effort from individuals, communities and governments.
Embracing its cultural legacy and ecological importance alongside the rich history of this magnificent Forest offers a greater opportunity for working together to ensure that one Canada’s most unique ecosystems can prosper on into future lineages. Let’s go explore the secrets and beauties of the Boreal, let our eyes and hearts wide open because it is time to get more clues about this great forset heritage that supports us all.
Also read: Paul Newman’s Rolex Daytona: The Iconic Timepiece with a Hollywood Legacy