Chemistry is at the heart of modern medicine, driving advancements in drug development, disease diagnosis, and medical research. The interaction between chemistry and medicine has revolutionized healthcare, leading to the discovery of life-saving drugs, innovative diagnostics, and a deeper understanding of the human body’s molecular processes. This article explores the pivotal role of chemistry in modern medicine, delving into drug design, diagnostic tools, and the ongoing quest for breakthroughs in healthcare.
Chemistry and Drug Discovery
- Drug Design and Molecular Structure: Chemistry plays a critical role in designing drugs that interact with specific molecular targets in the body. Researchers use computational chemistry to model and predict how drug molecules will interact with biological molecules.
- Medicinal Chemistry: Medicinal chemists optimize drug candidates, modifying their chemical structures to enhance efficacy, reduce side effects, and improve bioavailability.
- Drug Synthesis: Organic chemistry techniques are employed to synthesize pharmaceutical compounds efficiently and in large quantities.
- Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Chemistry helps determine how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body (pharmacokinetics) and how they produce therapeutic effects (pharmacodynamics).
Chemistry in Drug Formulation
- Pharmaceutical Formulation: Chemists develop drug formulations, such as tablets, capsules, and injections, to ensure the drug’s stability, release, and delivery to the target site.
- Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery: Nanoscale drug delivery systems use chemistry to encapsulate drugs within nanoparticles, improving drug solubility and targeting specific tissues.
Analytical Chemistry in Medicine
- Clinical Chemistry: Clinical laboratories use analytical chemistry techniques to analyze blood, urine, and other bodily fluids for diagnostic purposes, detecting diseases and monitoring treatment responses.
- Mass Spectrometry: Mass spectrometry is a powerful tool for identifying and quantifying molecules in complex biological samples, aiding in drug testing and disease diagnosis.
The Role of Chemistry in Diagnostics
- Molecular Diagnostics: Chemistry enables the development of molecular tests that detect genetic markers, pathogens, and biomarkers for diseases like cancer and infectious diseases.
- Imaging Agents: Radiopharmaceuticals and contrast agents used in medical imaging, such as positron emission tomography (PET) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), rely on chemistry to label and visualize specific tissues and structures.
Chemical Biology and Target Identification
- Proteomics and Genomics: Chemistry-driven approaches help identify potential drug targets by studying the interactions between proteins, genes, and small molecules.
- Chemical Probes: Chemical probes are small molecules that selectively bind to specific proteins, aiding in the study of their function and potential as drug targets.
Emerging Trends in Medicinal Chemistry
- Precision Medicine: Chemistry is central to the development of personalized therapies, where drugs are tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup and disease profile.
- Peptide and Protein Therapeutics: Advances in chemistry have enabled the design and synthesis of therapeutic peptides and proteins, expanding the range of treatable diseases.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
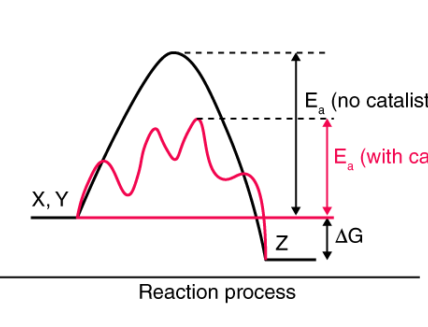
- Drug Resistance: Chemistry is vital in combating drug resistance by designing new drugs and optimizing treatment regimens.
- Ethical Drug Testing: The ethical use of chemistry in clinical trials and drug testing is essential to ensure patient safety and the validity of results.
Conclusion
Chemistry’s role in modern medicine is undeniable, with breakthroughs in drug discovery, diagnostics, and medical research improving the quality of healthcare worldwide. From the design of innovative drugs to the development of cutting-edge diagnostic tools, chemistry continues to drive advancements that benefit patients and contribute to our understanding of the complex mechanisms underlying health and disease. As technology advances and our knowledge of chemistry deepens, the partnership between chemistry and medicine promises to usher in a new era of healthcare, with more targeted and effective treatments, ultimately improving the lives of countless individuals.